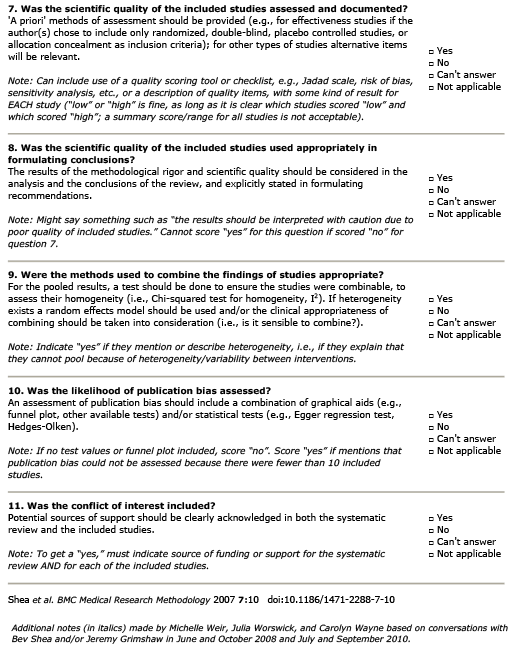
What is the evidence for collagen derivates (e.g. gelatin) in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee?
Summary
Patient Population:
A total of 1,187 participants were enrolled in 8 studies. Study size ranged from 30 participants to 389. The mean reported age was 57 years overall. 64.6% of participants were female. In 6/8 studies participants were limited to individuals with knee OA. In the remaining 2 studies, participants included individuals with knee or hip OA.
Intervention:
Collagen derivatives: undenatured collagen (UC), gelatin, or collagen hydrolysate (CH). Duration of treatment varied – 60 days to 24 weeks.
Comparison:
5/8 studies compared the use of CH to a placebo condition. Gelatine was compared to placebo, to CH and to alternative therapies. UC was compared to glucosamine + chondroitin. There were 8 studies identified for inclusion in the present review. All 8 were used in a narrative review. Only 3 provided data that could be used in a pooled analysis. The review reported serious methodological limitations to be present in all included studies. Allocation was rated to be adequate in only 3/8 studies and concealment of allocation in only 1 study. 2 studies met the requirement for blinding. 5/8 studies did not address missing data adequately. The problems identified in trial methodology was reflected in the GRADE ratings assigned.
Outcome:
- Pain: collagen hydrolysate vs. placebo (4 studies) – non-significant difference in favour of CH (SMD=-0.48; 95%CI -1.04 to 0.08).
- Pain: A single study compared CH with gelatin, but there were no clear between group differences reported for pain outcomes.
- Pain: A single study also compared CH with glucosamine. In this case, there was a significant improvement in pain associated with treatment with CH when compared to glucosamine.
- Pain: A single study examined the use of gelatin vs. placebo conditions. In that study, there was some effect in favour of gelatine for night pain and pain with movement.
- Function: collagen hydrolysate vs. placebo (3 studies) – non-significant difference in favour of CH (SMD=-0.74; 95%CI -2.58 to 1.09).
- Adverse Events: Adverse events were reported in 6 studies. Proportion of patients reporting adverse events ranged from 13-87% in the treatment groups and 9-87% in the control conditions. Most adverse events reported in the treatment conditions were mild to moderate gastrointestinal complaints: nausea,dyspepsia, diarrhea, flatulence. No trials reported significant between group differences for frequency of adverse events (Grade: moderate).