What is the evidence for ACL injury prevention programs?
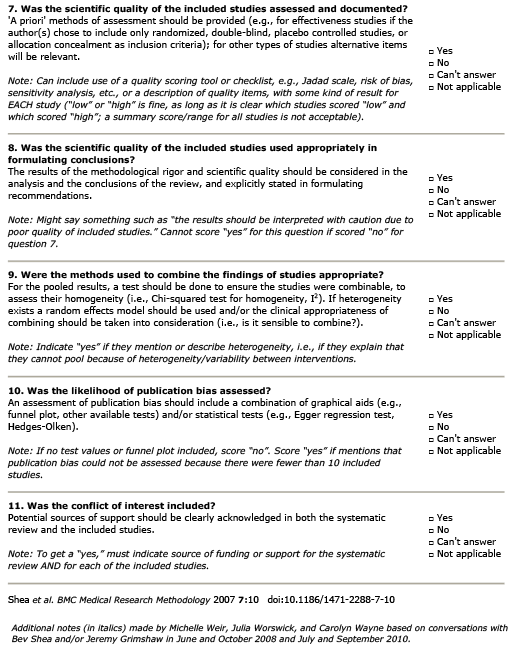
Summary
Patient Population:
Female athletes. Reported mean ages ranged from 14 – 22 years. Participants were involved in soccer, volleyball, basketball and handball.
Intervention:
Neuromuscular training designed to reduce incidence of ACL injury. Interventions employed mixed strategies that included stretching, plyometrics, weight-training/strength training, balance exercises, cardiovascular training, agility training, sport-specific drills, basic warm-ups, jump training, core stability Duration of training sessions ranged from 10 minutes – 90 minutes. Reported length of intervention was often based on the length of the competitive season (e.g. 12 weeks for soccer, 5 months for handball). Overall interventions ranged from 6 weeks – 9 months in length.
Comparison:
Number of ACL injuries in control and intervention groups.
Outcome:
-
The authors calculated a RRR for overall ACL injury of 0.438 (95% CI 0.289 to 0.555) for individuals assigned to treatment vs. control conditions.
-
There was a significant reduction in risk for non-contact ACL injury associated with intervention (RRR= 0.734; 95% CI 0.625, 0.811) for treatment vs. control conditions.
-
NNT for all ACL injuries = 120 athletes. NNT for non-contact ACL injuries = 108.