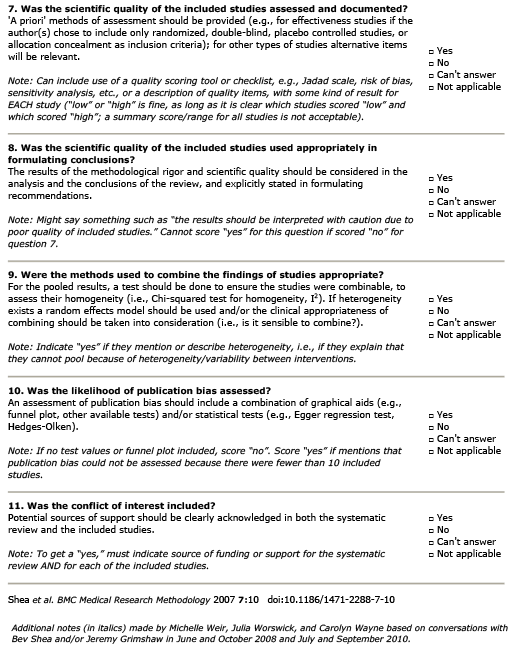
What is the evidence for extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the treatment of rotator cuff pathology?
Summary
Patient Population:
No information on the patient population was provided.
Intervention:
Low/medium/high energy extra-corporal shockwaves. Duration of treatment varied.
Comparison:
17 RCTs were identified for inclusion from various reviews and as single studies. 10 were considered to be of high quality, the remainder of low methodological quality. High ESWT was compared against: placebo, no treatment, low ESWT, medium ESWT, ultrasound and TENS.
Outcome:
- Pain and Function for calcific tendinosis: High ESWT vs. placebo (2 RCTs) – moderate evidence for short (3 months), medium (6 months) and long term (12 months).
- Pain and Function for calcific tendinosis: High ESWT vs. no treatment (1 RCT) – limited evidence for short term (3 months).
- Pain and Function for calcific tendinosis: High ESWT vs. low ESWT (1 RCT) – strong evidence for short term (3 months), and moderate evidence for medium (6 months) and long term (12 months).
- Pain, ROM, and Function for calcific tendinosis: High ESWT vs. medium ESWT (1 RCT) – no evidence to support one energy level over the other.
- Function for calcific tendinosis: High EWST vs. High EWST + ultrasound guided needling (1 RCT) – limited evidence in support of EWST + needling.
- Pain for calcific tendinosis: High ESWT vs. TENS (1 RCT) – limited evidence in favour of ESWT.
- Funciton for calcific tendinosis: Low ESWT vs. no treatment (1 RCT) – no evidence of benefit.
- Pain and Function for non-calcific tendinonsis: No evidence of benefit for any level of ESWT against any comparator.
Guideline Recommendations
| Source | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| ACOEM 2011 - for calcific rotator cuff tendinitis | Level A |
| ACOEM 2011 - for non-calcific rotator cuff tendinitis | Insufficient |
Outcomes Assessed
- Benefit
- Harm
- Inconclusive
High ESWT for Calcific Tendinosis
Pain
Function
High ESWT for Non-calcific Tendinosis
Pain
Function