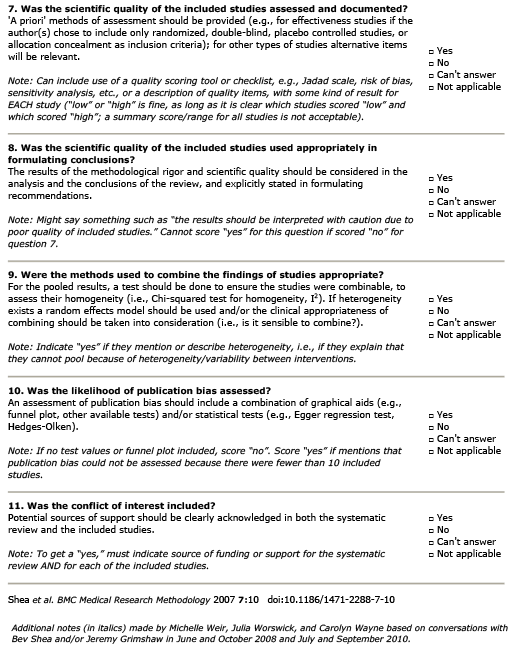
What is the evidence for nutritional supplementation in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee?
Summary
Patient Population:
No information on patient population was provided.
Intervention:
- Various micronutrients: selenium, zinc, copper, 6mg/day boron
- Vitamins: >75mg vitamin C, 3000mg/day vitamin b3 for 12 weeks, 4000 IU vitamin D3
- Nutracueticals: glucosamine
- ASU: Sterol-rich, lipid fraction from avocado or soybeans. 300mg/day.
- S-Adenosyl-Methionene (SAMe): 800-1600mg/day for 12 weeks.
- Bioflavonoid polyphenols: 500mg BID
- Ginger/ginger extract
Comparison:
Some studies compared supplementation to a placebo group, however, a large number did not report the comparison group. Most studies focused on knee OA, but occasionally also included hip and shoulder OA.
Outcome:
- Vitamin C: associated with reduced risk for cartilage loss, knee pain and OA progression (no comparison group listed).
- Vitamin E: in small clinical trials, associated with improved pain and stiffness (no comparison group listed).
- Vitamin D: conflicting evidence, may be more important in earlier stages of OA and younger patients (<60 y/o) – (no comparison group listed).
- Vitamin B3: 1 RCT was associated with improved mobility, reduced inflammation and reduction in NSAID use – similar results in a parallel group study using age matched controls (no comparison group listed).
- Selenium, Vitamin’s A, C, and E: 1 RCT was associated with improvement in pain and stiffness (vs. placebo).
- Boron: 1 RCT was associated with improved pain and function (vs. placebo).
- Glucosamine: associated with improvements in pain and function, reduces the risk for joint replacement and stabilizes cartilage degeneration (no comparison group listed).
- ASU: several small (non-RCT) studies were associated with improved pain and decreased NSAID use (vs. placebo).
- S-Adenosyl-Methionene (SAMe): 2 small studies associated with similar improvements to NSAID treatment with a longer effect than NSAIDs (no comparison group listed).
- Bioflavonoid polyphenols: 2 clinical trials were associated with improved joint function, a good safety profile and low toxicity, and (1 non-inferiority trial) as effective as naproxen (no comparison group listed for the 2 clinical trials).
- Ginger/ginger extract: 2 RCTs were associated with improved scores on WOMAC and VAS-pain index over short and long term (no comparison group listed).